Why Vitamin D Could Be the Missing Piece in Your Diabetes Management Plan

9 out of 10 diabetes patient has vitamin D insufficiency
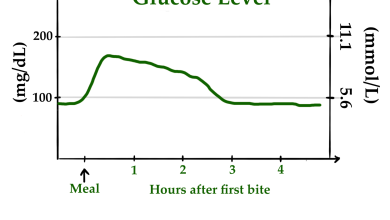
We have a lot of evidence showing that vitamin D can help improve insulin sensitivity, regulate blood sugar levels, and reduce the risk of complications associated with diabetes.
Firstly, let’s discuss the importance of vitamin D for people with diabetes. Vitamin D is a hormone that plays a crucial role in regulating the immune system, bone health, and glucose metabolism. Studies have shown that people with diabetes tend to have lower levels of vitamin D due to overuse by micro-inflammation, Starting with poor diet habits eg. Overconsumption of ultra-processed food, Snacking, night eating, Don’t know how to intermittent fasting. Poor sleep hygiene, overstress, lack of proper exercise, etc. This bad behavior contributes to insulin resistance and poor glycemic control.
A study published in the Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism found that people with type 2 diabetes who took vitamin D supplements for six months had a significant reduction in their HbA1c levels, a marker of long-term blood sugar control. Another study published in the Archives of Internal Medicine found that higher levels of vitamin D were associated with a lower risk of developing type 2 diabetes.
How can I raise vitamin D levels naturally?
Organic animal-based foods, such as fatty fish, animal fat, animal-organs esp. liver, egg yolks, and cheese are good sources of vitamin D.
What if I’ve diabetes or my blood test shows an insufficiency of vitamin D?
A daily intake of 2,000 IU for diabetes adults, but some people might need higher doses.(You can check vitamin D level with a blood test) It’s important to talk to your healthcare provider before starting any supplement regimen if you have any underlying conditions.
What is the best time to take vitamin D?
Vitamin D is a fat-soluble vitamin – so you’ll best absorb it alongside a fat-containing food, such as animal fat, almonds, peanut butter, or avocado.
When it comes to safety, vitamin D is generally considered safe when taken in recommended doses. However, excessive intake of vitamin D can lead to toxicity, which can cause nausea, vomiting, and kidney damage. It’s important to follow the recommended dosage and not exceed the tolerable upper limit of 4,000 IU per day.
Who needs to talk to a medical supervisor before using vitamin D?
People with hypercalcemia (high levels of calcium in the blood). Mostly found in hyperparathyroidism (overactivity of the parathyroid gland), and poor kidney function should not take vitamin D supplements without medical supervision.
Which one I should take between vitamin D2 and D3?
Vitamin D3 is the preferred form of vitamin D for supplementation because of its greater potency, faster metabolism, and wider availability. Check this out for more detail about the difference between vitamin D2 and D3.
In conclusion, vitamin D is an important supplement for people with diabetes. It can help improve insulin sensitivity, regulate blood sugar levels, and reduce the risk of complications associated with diabetes. However, it’s important to use it safely and in the appropriate dosage. Always talk to your healthcare provider before starting any supplement regimen.
References
1. Mitri, J., et al. (2011). Effects of vitamin D and calcium supplementation on pancreatic β cell function, insulin sensitivity, and glycemia in adults at high risk of diabetes: the Calcium and Vitamin D for Diabetes Mellitus (CaDDM) randomized controlled trial. Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism, 96(6), 1911-1919.
2. Pittas, A. G., et al. (2010). Vitamin D and calcium intake in relation to type 2 diabetes in women. Diabetes Care, 33(3), 650-656.
[elementor-template id=”60″]